BACK TO ALL
BACK TO ALL

One of the first devices for creating augmented reality was heavy, awkward and could crush a person’s head. Hanging from the ceiling on special mounts, it resembled a torture instrument from the Middle Ages. Although there are still many more improvements to be made, Augmented Reality is becoming cheaper, more comfortable, and more accessible for the average person day by day.
Augmented reality (AR) is seen as the next significant technological innovation that will impact each and every one of us. Many believe that AR will change the way we see the world and remove barriers by creating an additional 3D reality that we can take advantage of. In this article, we will look at AR’s key features to give you a better understanding of what might be just around the corner.
What is Augmented Reality and How Does It Work?
Augmented reality complements the physical world that we are experiencing in real time, by incorporating digital data with the help of portable devices such as tablets, smartphones or a special apparatus such as Google Glass or HoloLens. At this point, it needs to be mentioned that augmented reality should be distinguished from virtual reality and mixed reality. With augmented reality, virtual objects are projected onto real environments, while virtual reality is a world created by technical means, transmitted to a person through their sensory organs. Mixed (aka hybrid) reality combines both approaches.
To make it easy to remember the difference, simply imagine your friend wearing VR glasses, helplessly flailing his arms and bumping into walls. As far as AR is concerned, think back to 2016 when the whole world was obsessed with PokemonGO.
How does AR work?
To create an augmented reality, we need to use a processor, display, camera, and electronics, which determine the position, such as an accelerometer, GPS and compass. For example, touchscreen smartphone has the necessary kit for the owner of this gadget to plunge into the world of augmented reality.
Augmented reality applications work as follows:
- A special marker is used.
- A mobile device or computer reads the marker.
- The screen displays a layer of additional information.
Pattern recognition is quite straightforward. If an application needs to recognize a certain object, it consults a library of photos with this object in the server, identifies the general structure, color, and arbitrary parameters, assigning this object a specific action when it is detected.
Augmented reality markers are images or small objects that act as visual cues for the display of virtual information. Once augmented reality software is trained to recognize certain markers, the overlay of visual information will occur automatically.
The use of markers can be best illustrated through its use in films. For Peter Jackson's film trilogy, The Lord of the Rings, the character Gollum was created using markers. The monkeys in the most recent Planet of the Apes franchise were done in the same way. Actors in these films were required to wear special costumes with multiple markers on them that would allow every one of their movements to be tracked and transferred to the characters who were displayed virtually.
Now that you know the very basics of augmented reality, it may have become clear to you that we cannot put a marker on every object around us. Indeed, there is a need for a more advanced augmented reality system.
For this purpose, SLAM comes to the rescue. It is used to build maps in uncharted spaces with simultaneous control over the current location and distance covered. It is a tool that is well suited to using augmented reality systems on the move, as it lets the application know where the user is.
Here it is worth mentioning ARKit and ARCore. They are often referred to as SLAM, but in reality, they are its successors. So, let’s get this all straightened out.
ARKit is a Visual Inertial Odometry (VIO) system launched by Apple and presented as “the biggest AR platform in the world.” VIO is a system that tracks someone’s position and movements in their surroundings. The received data is calculated twice, in parallel, and then shown on your mobile device’s screen.
Such a two-way approach allows for more precise readings. Firstly, the Visual (camera) system tracks someone’s position with the help of a pixel on the camera sensor that matches a certain point in the real world. The second feature that ensures precision is the Inertial system, which consists of an accelerometer and gyroscope and tracks someone’s position. A Kalman Filter decides which system has provided more accurate information and publishes the position update via the ARKit SDK.
In turn, ARCore is Google’s platform for building augmented reality experiences. This system’s processes also consist of 2 essential steps. The first involves tracking the position of the mobile device in motion, and the second involves building an understanding of the surrounding environment. Considering this process, the phone’s camera recognizes particular points and their motion within a certain time period. As a result, the phone is able to calculate its position and orientation as it moves over distances. Furthermore, ARCore can identify flat surfaces and normal lighting. In other words, this system “reads” its surroundings to enable users to interact with any digital objects in a way that integrates seamlessly with the real world.
How is AR used?
The reason why augmented reality is so exciting is that it allows us to do day-to-day activities in a simpler way. Let’s look at some augmented reality examples that we are sure to see in the near future.
AR in education
With the help of AR, making education more in-depth and engaging is becoming a possibility. With this, students will be able to achieve better outcomes in subjects where complex objects often need to be imagined or are only encountered via 2D diagrams. Now students have the opportunity to interact with 3D visualizations of objects in subjects such as maths and science. Examining every detail of a human body or a geometrical shape will become a simple process with AR.
AR in healthcare
In addition to 2D illustrative training for medical school students, there is now an opportunity to see 3D models of patients. This can help a surgeon to react faster and act with greater precision during an operation. Visible anatomy using augmented reality is demonstrated by HoloLens’ HoloAnatomy.
AR in retail
No longer will a person have to measure the distances between objects in their home to see if a new item of furniture will fit or not. With AR, it is possible to select an item from an online catalog and virtually position it in your house. IKEA implemented this idea back in 2014.
AR in construction
Thanks to AR, visualization in architecture and construction moves to a qualitatively new level, allowing us to see the final result at the design stage, thereby reducing risks in the production process. The time-consuming practice of building model versions of constructions will also be a thing of the past. Augmented reality will shape the future of construction. By visualizing plans, builders can more easily go through what needs to be done step by step. Instead of looking through detailed and complex blueprints, they can take in the required information in a shorter space of time.
AR in the world of advertising
The commercial possibilities of augmented reality are so vast that it is almost impossible to conceive the boundaries of what is possible. In the advertising sphere, AR is proving groundbreaking. In 2009, readers could scan Esquire’s cover and see Robert Downey Jr come to life. What’s more, the wine brand “19 Crimes” allowed its consumers to come face-to-face with the infamous convicts on their bottles and hear their stories.
AR in the entertainment industry
Today, the most popular AR game is still PokemonGo. By combining augmented reality, geo-tracking and the popular Pokemon brand, it has reached unprecedented success. The game had been downloaded more than 800 million times by December 2018. Companies such as Lego and Disney have also been active in developing games using AR. Major toy manufacturers have expressed their intention to be a part of this exciting frontier as well.
AR in the military
The military has invested a lot in creating helmets which receive real-time information from the physical world while soldiers are in fighter planes or helicopters, and advise whether the surroundings are safe or not.
AR Devices
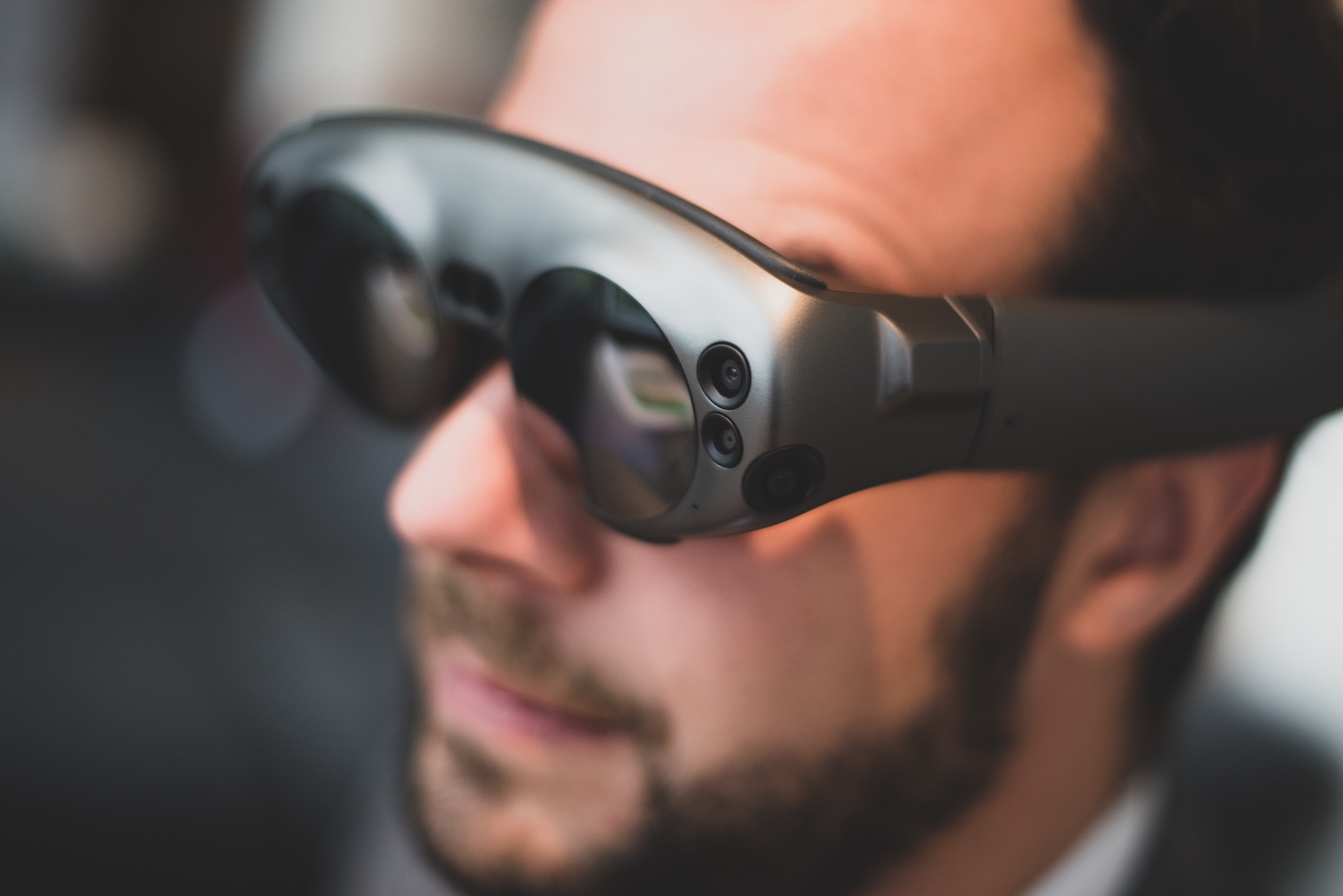

To experience augmented reality we need a special device. There are two options: AR glasses or headsets, and mobile devices.
The most vivid example of AR glasses is Google Glass. The brand of high-tech glasses originally excited people as they were able to take photos and shoot video on command, all of which was automatically sent to the cloud.
However, they didn’t become mainstream, mainly due to the high price and Google’s failure to convince users that the glasses would be needed on an everyday basis. There is, however, a happy ending. Google Glass is used today in industrial settings, bringing lots of value to the companies that have acquired them.
Microsoft has also attempted to conquer this arena by launching the HoloLens headset for business professionals. The headsets have received glowing reviews but are still not ideal for daily use.
Currently, the best chance of AR’s mainstream success lies with the Magic Leap headset. This device’s developers improved on all the mistakes made by competitors, and have developed a futuristic design similar to what is seen in the film Ready Player One. Despite quite a high price and a limited field of view, the Magic Leap device feels more comfortable, possesses a more intuitive display and offers greater immersion according to numerous reviews on the Internet.
For the time being, AR is still mostly found on mobile devices. This is due to the convenience they provide a common user with and a ready-made technical base mobile app developers deal with. The prevalence of mobile devices means that once AR becomes integrated with services we already use, it will also automatically become mainstream.
Aside from the AR gimmicks and games such as PokemonGO, it is obvious that there is an increasing amount of applications that want to change our reality, not just for novelty’s sake, but to make this world a better place in which to exist. At this very moment, you can use Google translate to help you read and understand street and shop signs when visiting a foreign country. The Sunseeker app has proved its worth for fans of hunting, and the Google Sky Map can foster users’ interest in astronomy, facilitating the search for stars and constellations.
Augmented Reality vs. Virtual Reality
With the emergence of technologies that have enabled augmented reality, a question arises: what is the difference between an augmented reality and a virtual one? Both can change the way we look at the world, and both promise tremendous growth. To make it plain to see, the biggest difference between augmented and virtual reality is:
- AR exists at the junction of the real and virtual worlds, while VR is fully computer generated.
- AR lets people interact with both worlds and see the difference between them, while with VR it is sometimes difficult to understand what’s real and what’s not.
- If you want to experience AR, your smartphone is your enough, while in the case of VR, you always need a special headset.
Is Augmented Reality the Future?
In a nutshell, augmented reality is no longer something futuristic, but a reality that is here and now. There are a huge number of opportunities for commercial use in the fields of education, industry, medicine, construction, commerce and even tourism. If properly implemented and maintained, it can become a useful and pleasant supplement to most human day-to-day activities.